- NEWS
NEWS
2020.08.14
Titanium Nitride Epitaxial Films as a Plasmonic Material Platform: Alternative to Gold
Titanium Nitride Epitaxial Films as a Plasmonic Material Platform: Alternative to Gold
ACS Photonics 6, 8, 1848–1854 (2019)
Wan-Ping Guo, Ragini Mishra, Chang-Wei Cheng, Bao-Hsien Wu, Lih-Juann Chen, Minn-Tsong Lin, and Shangjr Gwo*
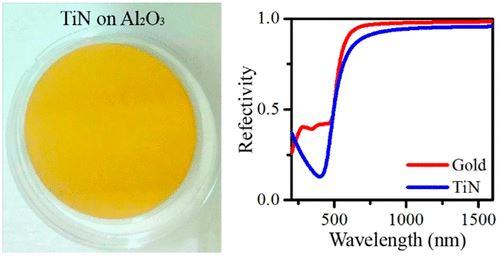
Titanium nitride (TiN) is an interesting refractory metallic compound which could replace gold as an alternative plasmonic material, especially for high temperature and semiconductor compatible applications. However, reported plasmonic properties of TiN films are so far limited by conventional growth techniques, such as reactive sputtering. In this work, we adopt the nitrogen-plasma-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) to grow single-crystalline, stoichiometric TiN films on sapphire substrates. The properties of as-grown TiN epitaxial films have been fully characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE), and surface plasmon polariton (SPP) interferometry. We have confirmed that MBE-grown TiN films exhibit excellent plasmonic properties to replace gold in the visible and near-infrared spectral regions. Measuring the real and imaginary parts of dielectric function by SE, it is also found that TiN is better than gold in the short-wavelength range (<500 nm), where gold suffers from strong loss due to interband transition. Contrary to the recent theoretical prediction that air is not able to stabilize SPP modes at the TiN surface, our surface plasmon interferometry data clearly show the presence of propagating SPP modes at the TiN/air interface. To demonstrate the unique plasmonic properties of MBE-grown stoichiometric TiN, we have fabricated TiN metasurfaces for the visible-spectrum applications.